Periodontitis Is a Serious Gum Disease
Periodontitis is a serious and potentially dangerous gum disease that affects the gums, teeth, and other structures that support the teeth. It is caused by bacteria that accumulate in plaque, which builds up on the teeth and gums. If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to tooth and implant loss.
The first signs of periodontitis are usually redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. These symptoms may be accompanied by bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth. As the disease progresses, pockets of infection form between the teeth and gums. This causes further inflammation and damage to the surrounding tissue. Eventually, if left untreated, periodontitis can cause bone loss around the teeth and even tooth loss.
Fortunately, periodontitis is preventable with good oral hygiene habits such as brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing once daily. Regular dental checkups are also important for early detection of any signs of gum disease so that treatment can begin before it becomes more severe. Treatment for periodontitis typically involves scaling (cleaning) below the gum line to remove plaque buildup as well as root planing (smoothing) to reduce bacterial growth in deep pockets between teeth and gums. In some cases antibiotics may be prescribed to help fight infection or surgery may be necessary to repair damaged tissue or bone structure around affected teeth.
Good oral hygiene habits are essential for preventing periodontitis but there are other factors that can increase your risk such as smoking or chewing tobacco products, diabetes, poor nutrition, certain medications or medical conditions like HIV/AIDS or cancer treatments that weaken your immune system making it harder for your body to fight off infection. Stress can also play a role in increasing your risk of developing gum disease so it’s important to practice stress-reducing activities like yoga or meditation on a regular basis.
If you have any concerns about your oral health or think you may have signs of periodontitis it’s important to visit your dentist right away for an evaluation so that appropriate treatment can begin before any further damage occurs. With proper care from both you and your dentist you can keep your smile healthy for years to come!
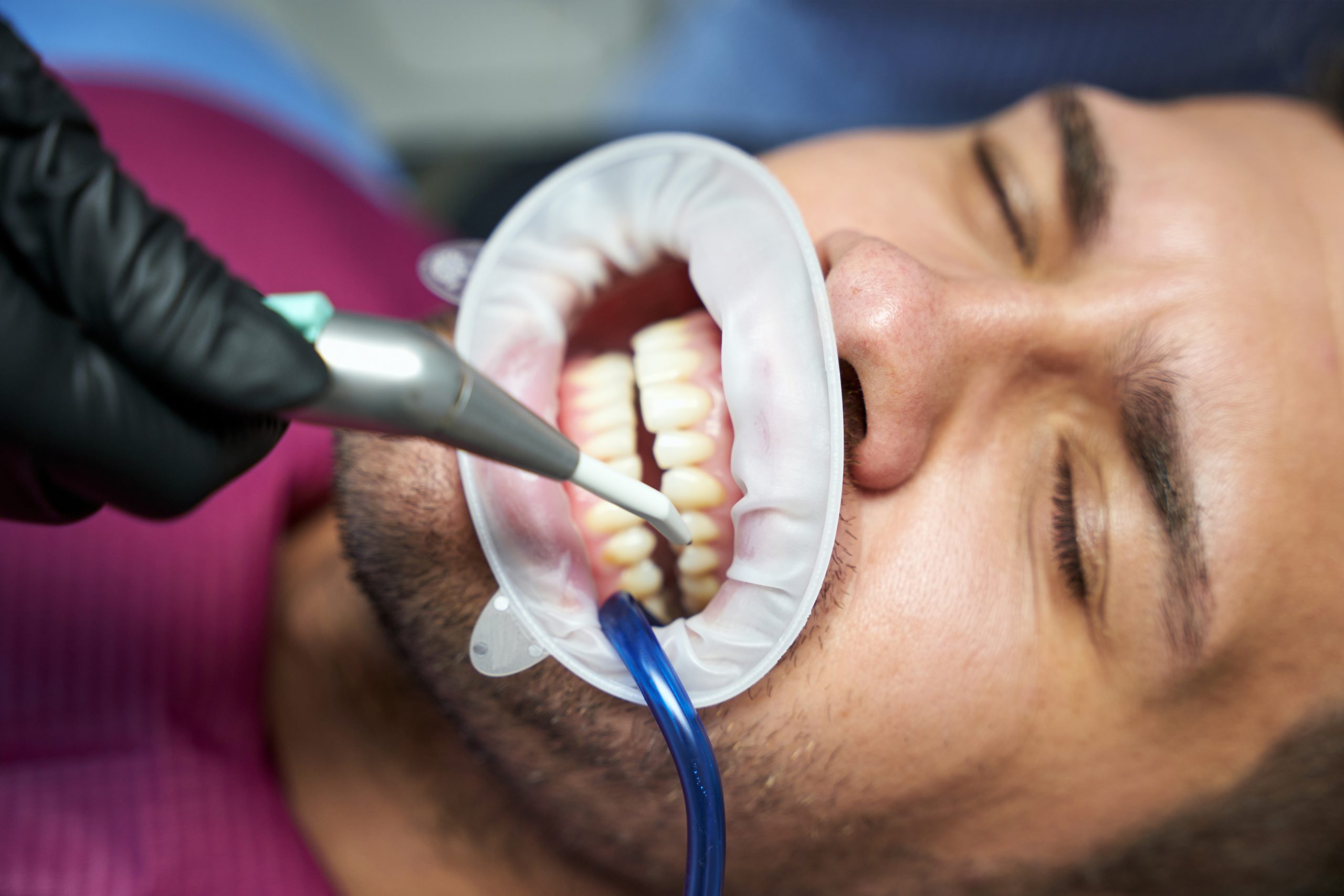
Chronic Periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis is a type of gum disease that affects the gums and bones that support the teeth. It is caused by bacteria in plaque, which builds up on the teeth and causes inflammation of the gums. If left untreated, chronic periodontitis can lead to tooth loss.
Symptoms of chronic periodontitis include red, swollen gums that may bleed when brushing or flossing; bad breath; receding gums; loose teeth; and pus between the teeth and gums. The disease can also cause pain when chewing or biting down on food.
The main cause of chronic periodontitis is poor oral hygiene. Plaque builds up on the teeth if it isn’t removed regularly with brushing and flossing. Other factors that increase your risk for developing chronic periodontitis include smoking, diabetes, stress, certain medications, genetics, and age.
If you think you may have chronic periodontitis, it’s important to see your dentist as soon as possible for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Your dentist will perform an examination to assess the severity of your condition and develop a personalized treatment plan for you. Treatment options for chronic periodontitis include scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), antibiotics to reduce inflammation and infection, surgery to repair damaged tissue or bone, laser therapy to kill bacteria below the gum line, or grafting to replace lost tissue or bone.
It’s important to practice good oral hygiene habits at home in order to prevent further damage from occurring due to chronic periodontitis. This includes brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing once daily, using an antiseptic mouthwash daily, avoiding smoking or tobacco use, eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins A & C (found in fruits & vegetables), drinking plenty of water throughout the day, visiting your dentist every 6 months for regular check-ups & cleanings, and scheduling regular dental exams & X-rays as recommended by your dentist.
By following these tips and working closely with your dentist on a treatment plan tailored specifically for you – you can successfully manage your condition & prevent further damage from occurring due to chronic periodontitis!
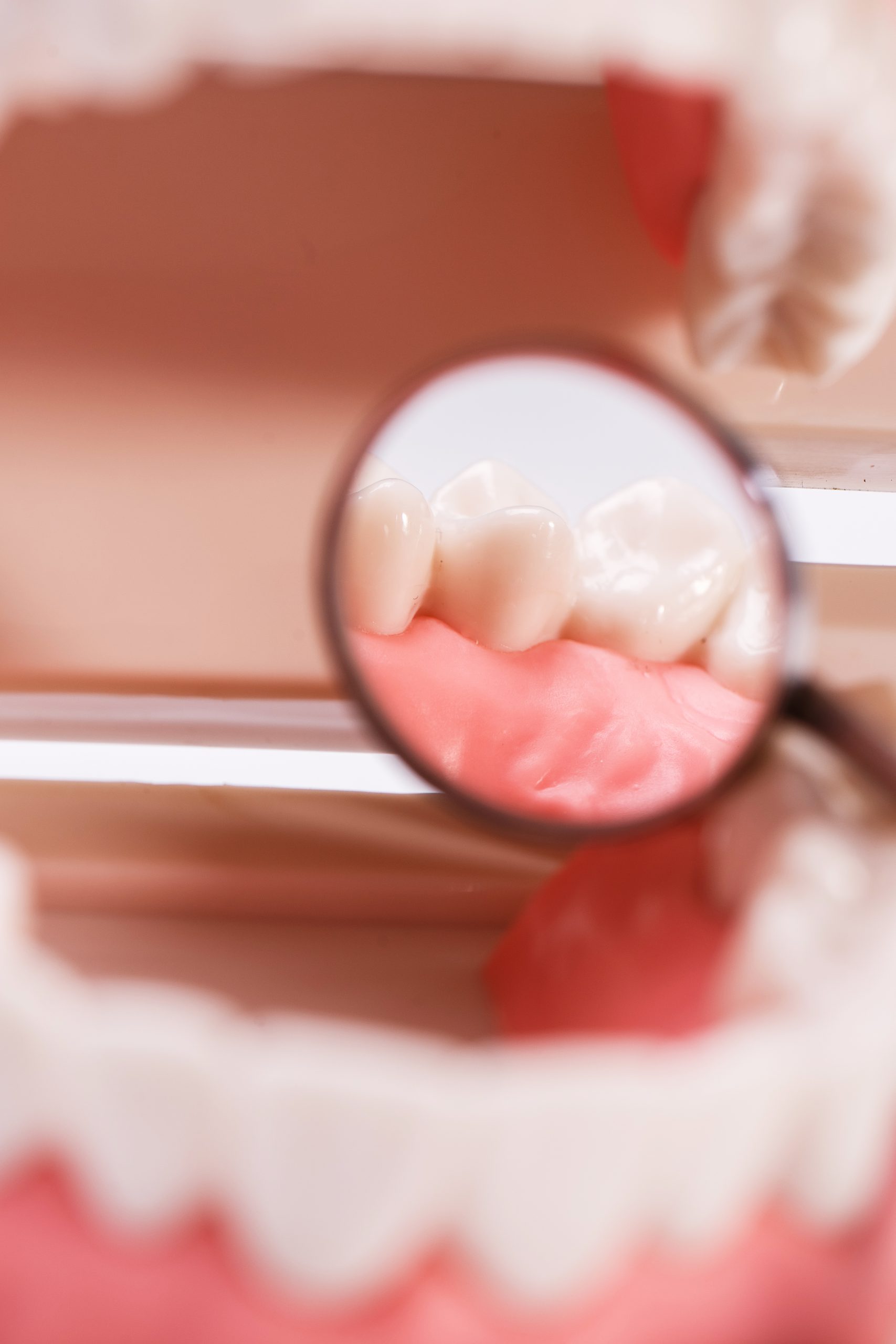
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases
Necrotizing periodontal diseases (NPDs) are a group of severe gum infections that can lead to the destruction of the soft tissue and bone supporting the teeth. NPDs are often seen in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or diabetes. They can also occur in otherwise healthy individuals who have poor oral hygiene or use tobacco products.
NPDs begin when bacteria invade the gums and cause inflammation. The inflammation causes the gums to become red, swollen, and tender. As the infection progresses, it can cause pockets to form between the teeth and gums where bacteria can collect and further damage the tissue. Eventually, these pockets deepen and destroy both the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth. This can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
Early diagnosis is key for successful treatment of NPDs. If you notice any signs of gum disease such as redness, swelling, or bleeding while brushing or flossing your teeth, it’s important to see your dentist right away for an evaluation. Your dentist will be able to diagnose NPDs based on your symptoms and a physical examination of your mouth.
Treatment for NPDs typically involves a combination of professional cleaning by your dentist along with antibiotics to fight off any infection present in your mouth. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged tissue or repair bone damage caused by NPDs.
Good oral hygiene is essential for preventing NPDs from occurring in the first place. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily will help keep bacteria levels low in your mouth so they don’t have a chance to cause an infection. Additionally, quitting smoking and avoiding other tobacco products can reduce your risk of developing NPDs significantly since tobacco use has been linked to an increased risk of gum disease in general.
If you’re at risk for developing NPDs due to an underlying medical condition or lifestyle choices like smoking, it’s important to visit your dentist regularly for checkups so they can monitor your oral health closely and catch any problems early on before they become more serious issues down the line. Taking good care of your teeth now will help ensure you maintain a healthy smile for years to come!
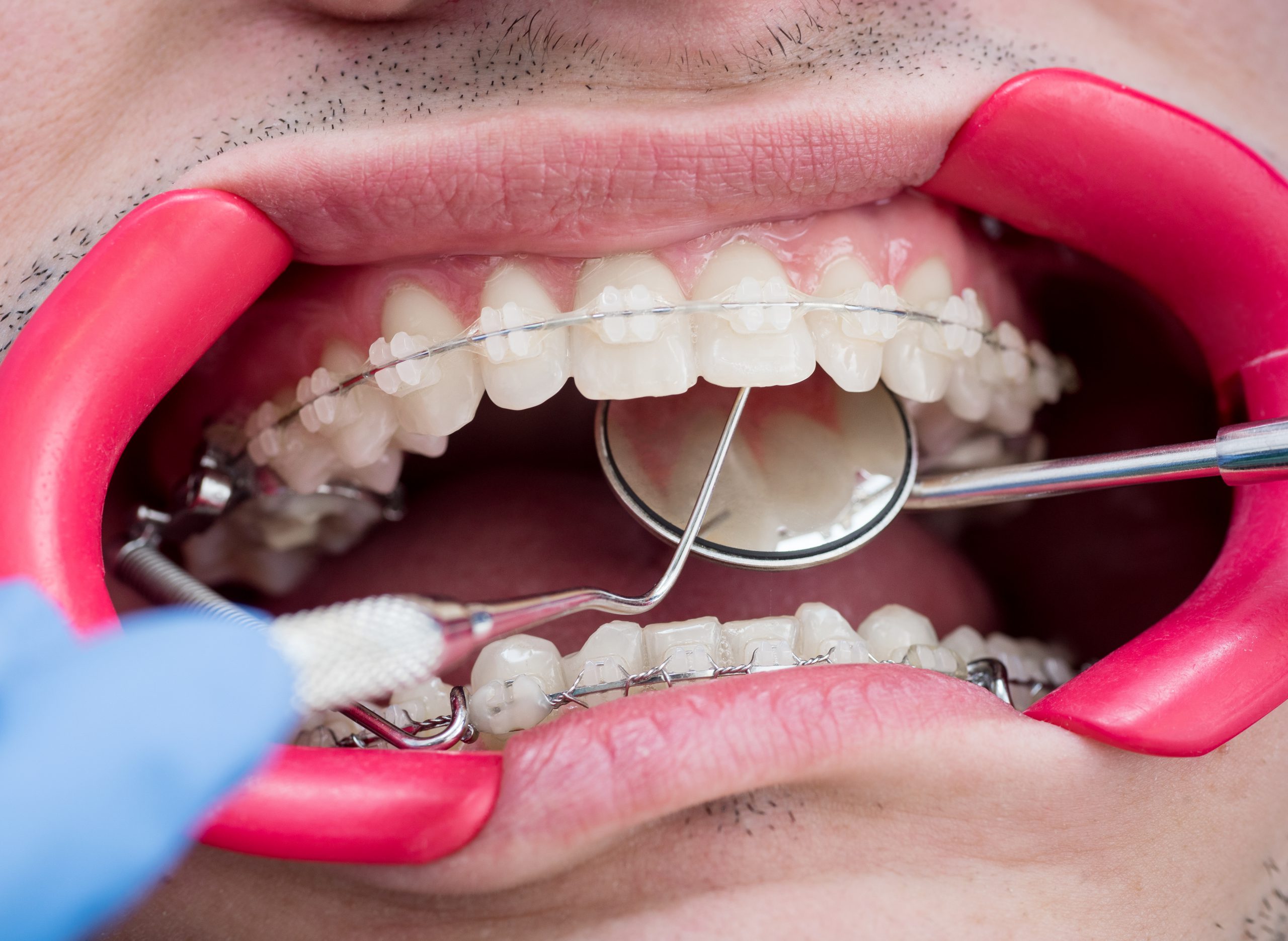
Abscesses of the Periodontium
Abscesses of the Periodontium are a type of infection that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the teeth. This infection is caused by bacteria that have been allowed to accumulate in pockets around the teeth, leading to inflammation and pain. If left untreated, abscesses can lead to more serious complications such as bone loss and tooth loss.
The most common cause of abscesses of the periodontium is poor oral hygiene. When plaque accumulates on the teeth, it can form a hard deposit called tartar which can trap bacteria and cause an infection. Other causes include gum disease, trauma to the mouth, smoking, or genetics.
The first sign of an abscess is usually a swollen area near the affected tooth accompanied by pain when biting down or chewing food. Other symptoms may include bad breath, redness or bleeding gums, sensitivity to hot or cold foods, fever, and pus drainage from the affected area.
If you suspect you have an abscess of the periodontium, it’s important to see your dentist right away for treatment. Treatment will depend on how severe your infection is but may include antibiotics to fight off any infection as well as draining any pus that has accumulated in order to reduce swelling and pain. In some cases, surgery may be necessary in order to remove any damaged tissue or bone that has been affected by the infection.
It’s important to practice good oral hygiene habits in order to prevent abscesses of the periodontium from occurring in the first place. This includes brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing once a day as well as visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Additionally, avoiding smoking and using tobacco products can help reduce your risk for developing this type of infection.
Abscesses of the periodontium are a serious dental condition that should not be ignored or taken lightly; if left untreated they can lead to more serious complications such as bone loss and tooth loss so it’s important to seek treatment right away if you suspect you have one. By practicing good oral hygiene habits such as brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing once a day as well as visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings you can help reduce your risk for developing this type of infection in the first place!

Gingivitis Is a Common Gum Disease
Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease that causes inflammation of the gums. It occurs when plaque builds up on the teeth, irritating the gums and causing them to become red, swollen, and bleed easily. Gingivitis can be reversed with good oral hygiene habits, but if left untreated it can lead to more serious forms of gum disease such as periodontitis.
Gingivitis is caused by bacteria in plaque that accumulate on the teeth near the gum line. Plaque is a sticky film that forms when bacteria combine with saliva and food particles. The bacteria in plaque produce toxins that irritate the gums, causing them to become inflamed and bleed easily. Poor oral hygiene habits such as not brushing or flossing regularly can also contribute to gingivitis.
The most common symptom of gingivitis is bleeding gums during brushing or flossing. Other symptoms may include redness, swelling, tenderness or receding gums. If you experience any of these symptoms it’s important to see your dentist for an evaluation so they can diagnose and treat your condition appropriately.
Treating gingivitis typically involves improving your oral hygiene habits such as brushing twice a day for two minutes each time and flossing daily. Your dentist may also recommend using an antibacterial mouthwash or other products to help reduce plaque buildup and prevent further irritation of the gums. In some cases, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics or recommend professional cleaning treatments such as scaling and root planing to remove plaque buildup below the gum line.
Preventing gingivitis starts with good oral hygiene habits including brushing twice a day for two minutes each time, flossing daily, using an antibacterial mouthwash, avoiding tobacco products, eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins A & C, drinking plenty of water throughout the day, visiting your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings, and managing any underlying medical conditions that could affect your oral health such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS.
Gingivitis is a common condition that can be reversed with proper treatment and preventive measures but if left untreated it can lead to more serious forms of gum disease like periodontal disease which can cause tooth loss if not treated promptly. It’s important to practice good oral hygiene habits every day to keep your teeth healthy and free from plaque buildup which can cause irritation of the gums leading to gingivitis. If you experience any signs or symptoms associated with this condition it’s important to see your dentist right away so they can diagnose and treat your condition appropriately before it progresses into something more serious like periodontal disease.
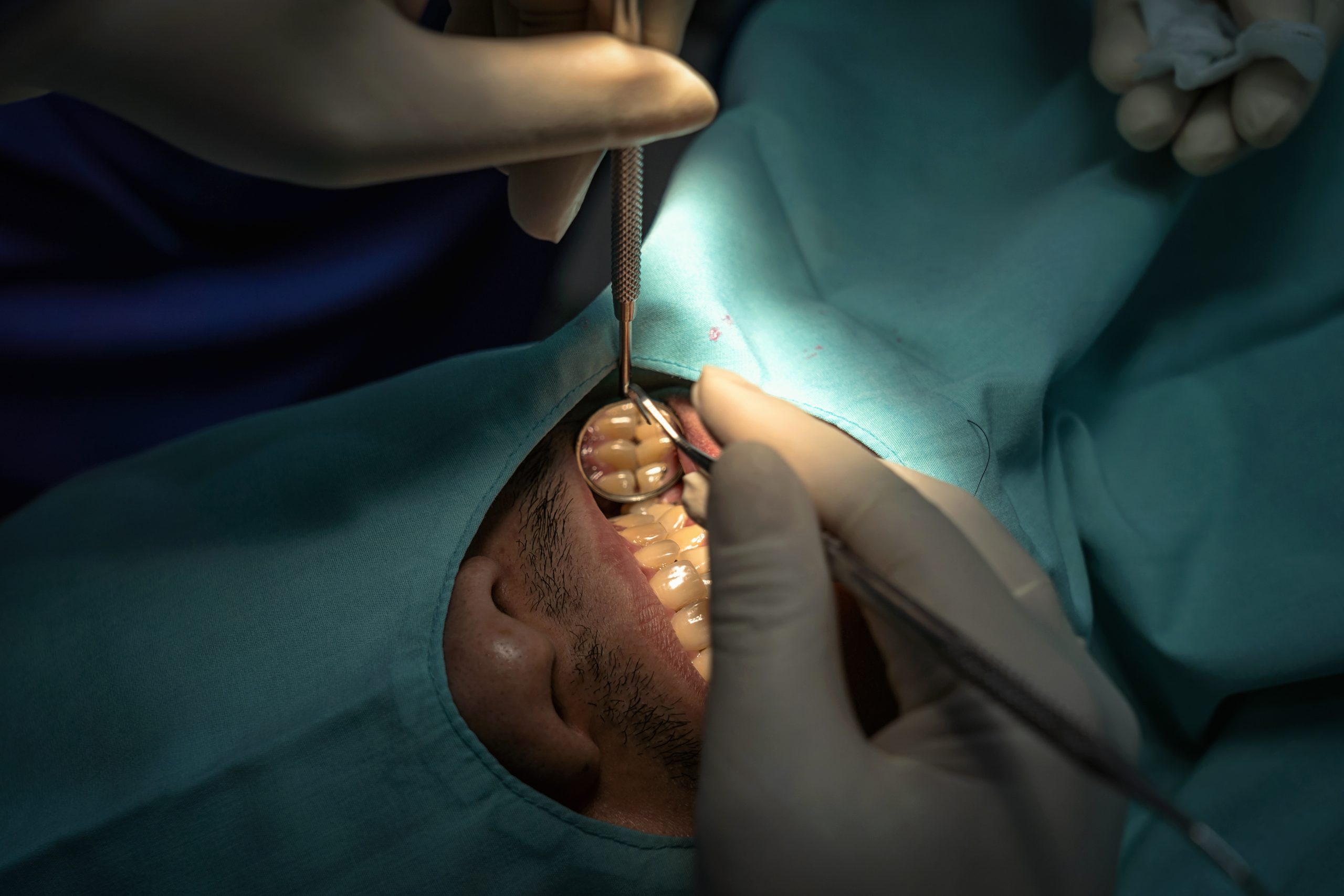
Gingival Enlargement Is a Gum Disease As Well
Gingival enlargement, also known as gingival hyperplasia, is a condition in which the gums become abnormally enlarged. It can occur in both children and adults, and is usually caused by an underlying medical condition or certain medications. While it may not be a serious health issue, it can cause discomfort and affect the appearance of your smile.
Gingival enlargement occurs when the gum tissue around your teeth becomes swollen and inflamed. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, genetics, certain medications, or an underlying medical condition such as diabetes or HIV/AIDS. In some cases, gingival enlargement may also be due to an allergic reaction to certain foods or products used in dental care.
The most common symptom of gingival enlargement is swollen and tender gums that may bleed easily when brushed or flossed. Other symptoms include redness and irritation of the gums, bad breath, difficulty eating or speaking due to pain or discomfort in the mouth area, and loose teeth due to weakened gum tissue. If left untreated, gingival enlargement can lead to periodontal disease (gum disease) which can eventually cause tooth loss if not treated promptly.
If you think you may have gingival enlargement it’s important to visit your dentist for a thorough examination so they can diagnose the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan accordingly. Treatment options will depend on the cause of your condition but may include improved oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly; prescription medications; surgical procedures; or lifestyle modifications such as quitting smoking or reducing stress levels.
Gingival enlargement can be embarrassing for those affected by it but there are ways to reduce its appearance while still treating the underlying cause effectively. Regular visits to your dentist are essential for maintaining good oral health and keeping your smile looking its best!
Gingival Recession
Gingival recession is a common dental condition in which the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away, exposing more of the tooth or its root. This can lead to increased sensitivity, tooth decay, and other oral health problems. It’s important to understand what causes gingival recession and how it can be treated.
The main cause of gingival recession is periodontal disease, which is an infection of the gums caused by bacteria in plaque. When plaque accumulates around the teeth, it irritates the gums and causes them to recede. Other factors that can contribute to gingival recession include aggressive brushing or flossing, misaligned teeth, genetics, tobacco use, hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause, and even certain medications.
If you’re experiencing any signs of gingival recession such as redness or tenderness in your gums or exposed roots on your teeth, it’s important to visit your dentist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Your dentist will be able to assess the extent of your condition and recommend a course of action that may include scaling and root planing (deep cleaning) to remove plaque buildup below the gum line; antibiotics to treat any infection; soft tissue grafts to replace lost gum tissue; crown lengthening surgery; or laser therapy.
It’s also important to practice good oral hygiene habits at home such as brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled brush and flossing once daily in order to keep plaque levels low and prevent further damage from occurring. Additionally, quitting smoking can help reduce your risk for developing periodontal disease and associated issues like gingival recession.
Gingival recession is a serious condition that requires prompt attention from your dentist in order to avoid further damage and complications down the road. If you think you may have this condition or are noticing signs of gum irritation or exposed roots on your teeth, don’t hesitate to contact your dentist right away for an evaluation and treatment plan tailored specifically for you.